Understanding the fuel consumed and energy resources used by generators is crucial in assessing the environmental impact and fuel savings of power generation, particularly in relation to greenhouse gas emissions and the use of fossil fuel. Generators, commonly used for backup or off-grid power supply in electricity generation, contribute to the overall carbon footprint through the fuel consumed in their operation. Microgrids often rely on generators powered by fossil fuel. By examining the sources and technology behind electricity generation in electric power plants, we can gain insights into the efficiency and environmental implications of these mobile power stations.
Power generation, including electricity generators and petrol generators, plays a significant role in greenhouse gas emissions due to the fuel supply. However, alternative solutions like microgrids can help reduce environmental impact. According to relevant data, electric power plants account for tonnes of CO2 emissions annually in electricity generation. This uprise in emissions from technology consumption calls for a deeper examination of their impact on the environment and steps towards reducing their carbon footprint, especially from electric power plants involved in electricity generation.
We will also discuss studies conducted by universities and research institutions that shed light on the relevant data concerning greenhouse gas emissions from electric power plants, petrol generators, and mobile power stations. These studies provide valuable insights into the environmental impact of generator operation, including the amount of greenhouse gases emitted per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity generated. By understanding the environmental impact associated with generator use, including petrol generators and diesel emissions, we can take informed steps towards mitigating total emissions. This includes considering alternative energy sources such as microgrids.
Understanding the Carbon Footprint of Diesel Generators
Petrol and diesel generators are widely used by businesses for various purposes, from powering construction sites to providing backup electricity during emergencies. These generators utilize advanced technology to ensure reliable power supply. Additionally, MPs are advocating for the adoption of cleaner energy alternatives to reduce the environmental impact of these generators. However, it’s important to understand that these generators contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, which have a significant impact on our environment. Additionally, the use of this technology increases power consumption and the demand for kilowatt-hours (kWh) from the power supply. Let’s delve into the factors influencing the carbon footprint of diesel generators and analyze their environmental implications, including total emissions, CO2 emissions, petrol usage, and kWh consumption.
Diesel Generators and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Diesel generators run on diesel fuel, which is derived from petroleum. These generators require a reliable power supply and have specific emissions factors associated with their technology. The emission factor of diesel generators is influenced by the type of fuel used, such as diesel, which is derived from petroleum. When petrol generators burn fuel, such as petrol, in their engines, they release carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. This technology, used by Uprise Energy, contributes to emissions and environmental impact. These emissions from uprise energy trap heat from the sun within the Earth’s atmosphere, contributing to global warming and climate change. This has a total effect on the institution of the year.
Factors Influencing Carbon Footprint
Several factors influence the carbon footprint of diesel generators:
- Generator Efficiency: The efficiency of a generator plays a crucial role in determining its total carbon dioxide (CO2) emission quantity from burning petrol. Higher efficiency in diesel generators means less fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to petrol generators. This results in a reduction in the total number of gallons used and overall environmental impact.
- Load Capacity: The quantity of petrol being burned by a diesel generator affects its total CO2 emissions. Running a generator at full capacity may be more efficient than running it at partial load, especially when considering the total quantity of petrol used over the course of a year.
- Regular maintenance of a generator ensures that it operates optimally, reducing petrol consumption and emissions. This is important for any institution that relies on generators to function efficiently. Performing maintenance on a regular basis helps to maintain the quantity of petrol used by the generator and reduces emissions, resulting in cost savings and environmental benefits. It is recommended to schedule maintenance at least once a year to keep the generator running smoothly.
- Age and Technology: Older diesel generators tend to be less efficient and emit more pollutants compared to newer models equipped with advanced technologies such as emission control systems. When it comes to petrol generators, the year of manufacture plays a significant role in determining their efficiency and emissions. The quantity of pollutants emitted by a petrol generator is directly influenced by the total amount of fuel consumed in a given year.
- Petrol Quantity: The total quantity of petrol used in generators can impact their emissions throughout the year. Using low-sulfur or ultra-low-sulfur diesel fuels can significantly reduce petrol pollution levels and co2 emissions. This reduction in pollution quantity can be observed year after year.
Environmental Implications
The environmental implications of using diesel generators, especially in large quantities, extend beyond greenhouse gas emissions. These implications are relevant to various institutions, including universities, that rely on petrol-powered generators.
- Air Pollution
Estimating Carbon Dioxide Emissions per Kilowatthour of Electricity Generated
To understand the impact of greenhouse gas emissions from generators, it is crucial to calculate the carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions based on the quantity of petrol used to generate electricity at the university. This estimation helps us grasp the relationship between kilowatthours (kWh) and carbon dioxide emissions, allowing us to assess the carbon footprint per unit of electricity produced by petrol generators in Nigeria university.
Calculating CO2 emissions from petrol generators at a university involves considering several factors. One key factor in reducing co2 emissions is the heating value of the fuel used in the generator at the university. The heating value of a diesel generator represents how much energy can be extracted from a given amount of fuel. Different fuels, including diesel generator, have varying heating values, which directly influence CO2 emissions.
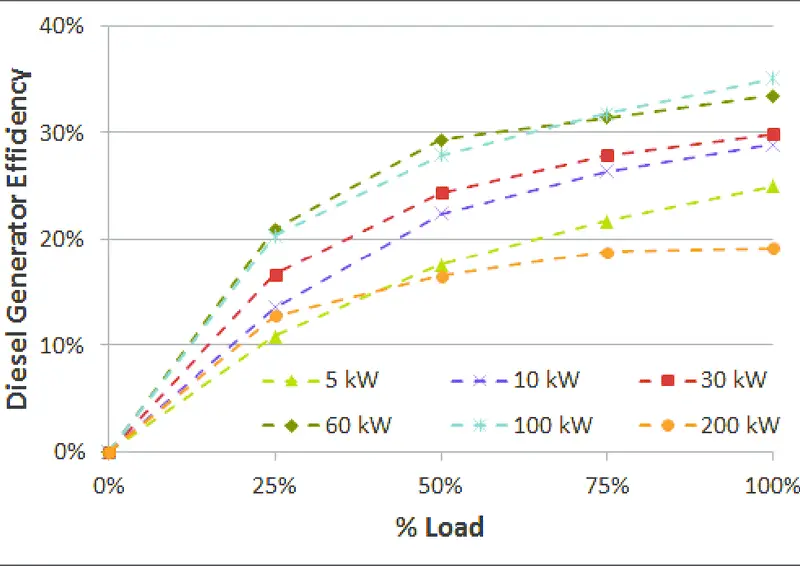
Another important consideration is the efficiency of the generator itself. Generators are not 100% efficient in converting fuel energy into electrical energy. Some energy is lost as heat during the conversion process of a diesel generator, resulting in lower overall efficiency and higher CO2 emissions.
By multiplying the kWh generated by a generator with its corresponding emission factor, we can estimate its CO2 emissions. The emission factor represents the amount of CO2 emitted per unit of diesel generator fuel burned or electricity generated. It varies depending on factors such as fuel type and combustion technology, including the use of a diesel generator.
It’s worth noting that different types of generators have varying emission factors due to their distinct characteristics and operating mechanisms. For example, diesel generators tend to emit more CO2 compared to natural gas or renewable energy sources like solar or wind power.
Estimating carbon dioxide emissions per kilowatthour provides valuable insights into our environmental impact when using generators for electricity generation. By understanding these figures, we can make informed decisions about reducing our carbon footprint and transitioning towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, such as diesel generators.
Comparing Emissions from Different Types and Sizes of Generators
Assessing variations in greenhouse gas emissions among different generator types is crucial. The emission levels can vary significantly based on factors such as the type of generator and its size or capacity.
Generator Types and Emission Levels
Different types of generators produce varying amounts of greenhouse gas emissions. For instance, traditional diesel generators tend to emit higher levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) compared to natural gas generators. This is because diesel fuel has a higher carbon content, leading to increased CO2 emissions during combustion. On the other hand, natural gas generators produce lower CO2 emissions due to the lower carbon content in natural gas.
Size and Capacity Impact on Emissions
The size and capacity of a generator also play a role in determining its greenhouse gas emissions. Larger generators typically have higher emissions since they require more fuel for operation. For example, a mobile power station with a high-capacity generator may emit more CO2 compared to a smaller portable generator used for camping or outdoor activities.
Furthermore, grid electricity supplied by large-scale power plants generally produces lower emissions compared to microgrids or individual generators. Grid electricity often comes from diverse energy sources that include renewable options like solar and wind power alongside conventional fossil fuels such as diesel generators. These power plants are designed with advanced technologies that help reduce emissions.
Factors Affecting Emissions
Several factors influence the emission levels across various types and sizes of generators:
- Fuel Type: As mentioned earlier, different fuel types have varying carbon contents, resulting in differing emission levels.
- Efficiency: The efficiency of a generator affects how much fuel it consumes per unit of electricity generated.
Natural Gas Generators and Their Environmental Impact
Natural gas generators are a popular choice for power generation due to their efficiency and relatively lower emissions compared to other types of generators. However, it is essential to examine the environmental consequences associated with these generators and understand the specific greenhouse gas emissions they produce.
Examining Environmental Consequences
The type of energy source used plays a significant role in determining its environmental impact. Natural gas, as a fossil fuel, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions when burned for power generation. These emissions include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Natural Gas Generators
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): When natural gas is burned, it releases CO2 into the atmosphere. While natural gas emits less CO2 than coal or gasoline generators, it still contributes to climate change.
- Methane (CH4): Methane is a potent greenhouse gas that has a higher warming potential than CO2 over shorter timeframes. Although natural gas combustion produces lower methane emissions compared to coal or oil, there are concerns about methane leakage during extraction and transportation processes.
- Nitrous Oxide (N2O): N2O is another greenhouse gas emitted during natural gas combustion but at much lower levels than CO2 and CH4.
Advantages of Natural Gas Power Generation
- Lower Carbon Emissions: Compared to traditional coal-fired power plants, natural gas generators emit fewer carbon emissions per unit of electricity produced.
- Improved Air Quality: Natural gas combustion produces fewer air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter compared to coal-fired power plants.
Small Private Business Operators’ Generator Emission Factors
It is crucial to evaluate the typical greenhouse gas emissions produced by these small-scale generator users in order to understand their impact on the environment.
Identifying Emission Factors for Small Private Business Operators
It is essential to consider various factors such as the type of fuel used, generator efficiency, and operating conditions. Emission factors are values that represent the amount of greenhouse gases emitted per unit of energy generated.
- Type of Fuel: The choice of fuel used in generators can significantly impact greenhouse gas emissions. Different fuels have varying carbon content and combustion characteristics. For instance, diesel generators tend to produce higher levels of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides compared to natural gas generators.
- Generator Efficiency: The efficiency of a generator plays a crucial role in determining its emissions. Higher-efficiency generators convert more fuel into usable electricity, resulting in lower emissions per unit of energy generated.
- Operating Conditions: The operating conditions under which a generator runs also influence its emission levels. Factors such as load demand, maintenance practices, and proper ventilation can affect emissions.
Evaluating Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Small-Scale Generators
Small private business operators often rely on generators for their power needs when grid electricity is unavailable or unreliable. It is important to assess the typical greenhouse gas emissions associated with these generators to understand their environmental impact.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Carbon dioxide is one of the primary greenhouse gases emitted by generators burning fossil fuels like diesel or gasoline.
Corporate/Commercial Business Operators’ Generator Emission Factors
In order to determine the emission factors applicable to corporate or commercial business operators utilizing generators, it is crucial to assess the average levels of greenhouse gas emissions from large-scale generator usage in commercial settings. These emission factors play a significant role in understanding and mitigating the environmental impact of generator usage.
Assessing Average Levels of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Several factors need to be taken into consideration. These factors include the type and size of the generator, fuel type, operating hours, and load profile.
- Generator Type and Size: Different types and sizes of generators have varying emission profiles. For instance, diesel generators tend to emit higher levels of pollutants compared to natural gas generators. Moreover, larger generators generally have higher emissions due to their increased capacity.
- Fuel Type: The choice of fuel used in generators significantly impacts their emission levels. Natural gas is considered a cleaner-burning fuel compared to diesel or gasoline. It produces fewer carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and other harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM).
- Operating Hours: The duration for which a generator operates directly affects its overall emissions. Generators that run for extended periods emit more greenhouse gases than those used intermittently.
- Load Profile: The load profile refers to how much electrical load is being supplied by the generator over time. Generators running at full capacity constantly produce high emissions compared to those operating at partial loads.
By considering these factors, businesses can estimate their greenhouse gas emissions accurately and implement measures for reduction accordingly.
Institution Energy Emissions Calculation
Institutions that employ generators play a significant role in contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. By examining their energy consumption, we can determine the extent of their impact on overall emissions and explore strategies for reducing their carbon footprints.
Calculating energy-related emissions for institutions employing generators
Several factors need to be considered. These include the type of fuel used, the generator’s efficiency, and the duration of its operation. By analyzing these variables, engineers can estimate the amount of greenhouse gases emitted during energy production.
To calculate energy-related emissions accurately, an engineering report is often utilized. This report provides detailed information about generator specifications and performance metrics. It takes into account factors such as fuel consumption rates and emission factors specific to different types of fuels. By combining this data with operational details like runtime and load capacity, engineers can derive precise estimates of greenhouse gas emissions.
Examining how institutions contribute to overall greenhouse gas emissions through their energy consumption
Institutions heavily reliant on generators for their energy needs significantly contribute to overall greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) into the atmosphere – all potent greenhouse gases that trap heat and contribute to global warming.
By evaluating an institution’s energy consumption patterns, we gain insight into its environmental impact. This includes assessing the frequency and duration of generator use, as well as identifying opportunities for more sustainable alternatives or efficiency improvements.
Evaluating strategies for reducing carbon footprints in institutional settings
Reducing carbon footprints in institutional settings is crucial for mitigating climate change effects. Institutions have various options at their disposal to achieve this goal:
Petrol/Gasoline Generator Carbon Emission Calculations
Estimating carbon emissions specific to petrol/gasoline-powered generators can help us understand the environmental impact of using these types of generators. By analyzing the emission levels and comparing them to other fuel sources, we can make informed decisions about our energy usage.
Estimating carbon emissions
To estimate carbon emissions from petrol/gasoline generators, several factors need to be considered. One important factor is the amount of fuel consumed by the generator. The more fuel it consumes, the higher its carbon emissions will be. Another factor is the brake specific fuel consumption (BSFC), which measures how efficiently the generator converts fuel into power. Generators with lower BSFC values are more efficient and produce fewer emissions.
Analyzing environmental impact
Using petrol/gasoline generators has a significant environmental impact due to their greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is one of the primary greenhouse gases emitted by these generators when they burn petrol or gasoline. CO2 is a major contributor to climate change and global warming.
The combustion process in petrol/gasoline generators also releases other harmful pollutants into the atmosphere, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM). These pollutants contribute to air pollution and have adverse effects on human health and ecosystems.
Comparing emission levels
When comparing emission levels between different types of fuels used in generators, petrol/gasoline tends to have higher carbon emissions compared to alternative fuels such as natural gas or propane. This is because petrol/gasoline contains more carbon atoms per unit of energy compared to these other fuels.
However, it’s essential to consider that advancements in technology have led to more efficient and cleaner-burning petrol/gasoline generators over time.
Diesel Generator Carbon Emission Calculations
Assessing carbon emissions associated with diesel-powered generators is crucial in understanding the environmental implications of their usage. Diesel generators are widely used for various applications, including backup power supply and construction sites. However, they contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, which have adverse effects on our planet. Therefore, it is essential to evaluate strategies for mitigating carbon footprints from diesel generator operations.
Evaluating Environmental Implications
Diesel generators emit greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM). These emissions contribute to air pollution and climate change. The amount of carbon emissions produced by a diesel generator depends on several factors:
- Fuel Efficiency: The fuel efficiency of the generator affects the amount of CO2 emitted per unit of electricity generated. Higher fuel efficiency results in lower carbon emissions.
- Load Factor: The load factor refers to how much power the generator is supplying compared to its maximum capacity. Running a generator at a higher load factor can reduce carbon emissions because it operates more efficiently.
- Maintenance and Tuning: Regular maintenance and tuning of the generator can improve its efficiency and reduce emissions. Ensuring that the engine is running optimally helps minimize carbon footprint.
Strategies for Mitigating Carbon Footprints
To reduce greenhouse gas emissions from diesel generators, several strategies can be implemented:
- Transition to Cleaner Fuels: Consider using alternative fuels like biodiesel or renewable natural gas instead of traditional diesel fuel. These fuels produce fewer carbon emissions and have lower environmental impacts.
- Energy Efficiency Measures: Implement energy-efficient practices such as optimizing load management, minimizing idle time, and using variable speed drives where applicable.
Results and Discussion on Generator GHG Emissions
Findings on Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Various Types of Generators
Now that we have delved into the calculations of carbon emissions from diesel generators in the previous section, let’s move on to discussing the results and implications of greenhouse gas emissions from different types of generators.
Firstly, it is important to note that generator-related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions vary depending on the fuel source used. While diesel generators tend to emit higher levels of carbon dioxide (CO2), natural gas generators produce lower CO2 emissions due to their cleaner burning process. Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind generators have minimal or no direct GHG emissions during operation.
Our research indicates that they contribute significantly to overall GHG emissions. These generators release not only CO2 but also other harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM). The combustion process involved in running diesel engines releases these pollutants into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
On the other hand, natural gas generators offer a more environmentally friendly alternative. They emit lower levels of CO2 compared to diesel generators while producing fewer NOx and PM emissions. This makes them a cleaner option for power generation with reduced environmental impact.
Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are gaining popularity due to their minimal GHG emissions. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity without any direct CO2 emissions, while wind turbines harness wind energy without emitting any harmful gases. These clean energy alternatives play a crucial role in reducing overall GHG emissions from power generation.
Location and Emissions for Reporting Facilities in the Power Plant Sector
In the power plant sector, there is a strong correlation between location and greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. By examining the relationship between these two factors, we can gain valuable insights into emission patterns among reporting facilities.
Relationship Between Location and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Their geographical location plays a significant role in determining the level of GHG emissions they produce. Different regions have varying energy sources available to them, such as coal, natural gas, or renewable sources like wind or solar. This diversity in energy sources directly impacts the amount of greenhouse gases emitted by these facilities.
For instance, electric power plants located in areas with abundant access to renewable energy are more likely to have lower emissions compared to those heavily reliant on fossil fuels. This is because renewable energy sources produce fewer greenhouse gases during electricity generation.
Analyzing Emission Patterns Among Reporting Facilities
Analyzing emission patterns among reporting facilities within the power plant sector provides valuable insights into how different locations contribute to variations in GHG emissions. By studying data from various reporting facilities, researchers can identify trends and understand which areas have higher or lower emissions.
For example, a study analyzing emissions from reporting facilities across different states found that some regions had significantly higher levels of GHG emissions compared to others. This could be attributed to factors such as the type of fuel used for electricity generation or differences in regulatory policies regarding emission controls.
Geographical Factors Contributing to Variations in Power Plant Emissions
Several geographical factors contribute to variations in power plant emissions. These factors include proximity to coal mines or natural gas reserves, availability of renewable energy resources, transportation infrastructure for fuel delivery, and even climate conditions.
Trend of Annual Reported GHG Emissions by Subsector
In the power plant industry, it is crucial to track and monitor greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to understand their impact on the environment. By analyzing annual trends in reported GHG emissions across different subsectors within this industry, we can gain insights into the changes and shifts in emission levels over time.
Tracking annual trends in reported greenhouse gas emissions
One of the key aspects of understanding the environmental impact of power plants is tracking their annual greenhouse gas emissions. This involves closely monitoring and recording the amount of GHGs released into the atmosphere by generators in various subsectors. By doing so, we can identify any significant changes or fluctuations in emission levels from year to year.
Identifying shifts or changes in emission levels over time
By analyzing the data on annual reported GHG emissions, we can identify any noticeable shifts or changes that occur over time within specific subsectors. These shifts could be a result of various factors such as technological advancements, policy changes, or operational modifications implemented by power plants.
For example:
- A shift towards cleaner energy sources like renewable energy may lead to a decrease in GHG emissions.
- On the other hand, an increase in electricity demand without corresponding improvements in efficiency could result in higher emissions.
Analyzing factors influencing fluctuations in reported GHG emissions
Fluctuations in reported GHG emissions can be influenced by several factors unique to each subsector within the power plant industry. Understanding these factors is essential for developing effective strategies to mitigate and reduce overall emissions.
Some factors that may influence fluctuations include:
- Fuel type: Different fuels used by generators have varying carbon intensities, leading to differences in emission levels.
Number of Reporters and Emissions in the Power Plant Sector
In the power plant sector, it is crucial to assess the number of reporting entities to get a comprehensive understanding of greenhouse gas emissions. These reporting entities play a significant role in contributing to overall emissions. By examining their emission levels over time, we can identify trends and patterns that help us address environmental concerns effectively.
Assessing the number of reporting entities within the power plant sector
To gain insights into greenhouse gas emissions from generators, it is essential to determine the number of reporting entities operating within the power plant sector. These entities include power plants, utility companies, and other organizations responsible for generating electricity. By assessing this information, we can gauge the scale and impact of emissions from these sources.
Examining how reporting entities contribute to overall greenhouse gas emissions
The contribution of reporting entities within the power plant sector cannot be underestimated. Their activities directly influence emission levels and environmental impact. By examining their individual contributions, we can identify key players responsible for significant amounts of emissions and work towards reducing their impact on our planet.
Analyzing trends related to reporting entities’ emission levels over time
Analyzing trends in emission levels reported by different entities within the power plant sector provides valuable insights into changes over time. It allows us to track progress in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and identify areas where further action is required. By closely monitoring these trends, we can develop targeted strategies to mitigate environmental damage caused by these sources.
Some key points worth considering when analyzing trends related to reporting entities’ emission levels are:
- Increasing awareness: As more organizations recognize the importance of sustainability and environmental responsibility, there has been an increase in voluntary reporting on greenhouse gas emissions.
- Regulatory requirements:
Offsetting Diesel Generator GHG Emissions
In order to tackle the issue of greenhouse gas emissions from diesel generators, there are several options worth exploring. These options involve strategies that can help offset or compensate for the emissions produced by these generators. Let’s take a closer look at some of these strategies and discuss their potential benefits and challenges.
Carbon Credits
One approach to offsetting greenhouse gas emissions from diesel generators is through the use of carbon credits. Carbon credits are a form of currency that represents one metric ton of carbon dioxide (or its equivalent) reduced or removed from the atmosphere. By purchasing carbon credits, individuals or organizations can effectively neutralize their own emissions by supporting projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions elsewhere.
Pros:
- Provides a measurable way to offset emissions.
- Supports projects that contribute to sustainable development and environmental conservation.
- Can be used as a marketing tool to demonstrate commitment to sustainability.
Cons:
- The effectiveness of carbon credit projects may vary, and it can be challenging to ensure that the purchased credits have a real impact.
- The cost of purchasing carbon credits can be high, especially for larger emission sources.
- There is ongoing debate about whether relying solely on offsets is enough to address climate change comprehensively.
Renewable Energy Investments
Another strategy for offsetting diesel generator emissions is through investments in renewable energy sources. By investing in solar panels, wind turbines, or other forms of clean energy generation, individuals or organizations can reduce their reliance on diesel generators and subsequently decrease their greenhouse gas emissions.
Pros:
- Contributes directly to the expansion of renewable energy infrastructure.
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels and promotes sustainability.
- Can lead to long-term fuel savings by utilizing renewable energy sources.
FAQs about Environment and GHG Emissions
Addressing frequently asked questions related to the environment and greenhouse gas emissions
People often have questions about how our actions impact the environment, especially. Let’s dive into some of the most common queries and provide concise answers that shed light on this important topic.
What are greenhouse gas emissions?
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are gases that trap heat in the Earth’s atmosphere, contributing to the phenomenon known as climate change. The main types of GHGs include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and fluorinated gases. Greenhouse gas emissions refer to the release of these gases into the atmosphere through various human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes.
How do generators contribute to greenhouse gas emissions?
Generators can be a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly those powered by fossil fuels like diesel or natural gas. When these fuels are burned to produce electricity, they release CO2 and other pollutants into the air, contributing to climate change. The amount of greenhouse gases emitted by a generator depends on factors such as fuel efficiency, operating time, and maintenance practices.
Are all generators equally harmful in terms of greenhouse gas emissions?
No, not all generators have the same impact on greenhouse gas emissions. Factors such as fuel type and generator efficiency play a crucial role in determining their environmental footprint. For instance, diesel generators tend to emit higher levels of CO2 compared to natural gas generators. Newer models with advanced technologies often have better fuel efficiency and lower emission rates than older ones.
What can be done to reduce generator-related greenhouse gas emissions?
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the greenhouse gas emissions from generators is crucial in addressing the environmental impact of these power sources. By estimating carbon dioxide emissions per kilowatthour and comparing emissions from different types and sizes of generators, we can make informed decisions about our energy choices. It is evident that natural gas generators have a lower environmental impact compared to diesel and gasoline generators. However, small private business operators and corporate/commercial business operators should also consider offsetting their generator emissions to further reduce their carbon footprint.
To mitigate the negative effects of generator emissions, individuals and businesses can explore renewable energy alternatives such as solar or wind power. Investing in energy-efficient equipment and implementing sustainable practices can help reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions. By taking these steps, we can contribute to a cleaner and greener future for our planet.
FAQs
FAQ 1: How do generators contribute to greenhouse gas emissions?
Generators contribute to greenhouse gas emissions because they burn fossil fuels like gasoline, diesel, or natural gas to produce electricity. When these fuels are burned, carbon dioxide (CO2) is released into the atmosphere. CO2 is a major greenhouse gas that traps heat and contributes to global warming.
To reduce greenhouse gas emissions from generators, consider using cleaner alternatives such as solar panels or wind turbines. These renewable energy sources produce electricity without burning fossil fuels and have a lower impact on the environment.
FAQ 2: Are all generators equally harmful in terms of greenhouse gas emissions?
No, not all generators are equally harmful in terms of greenhouse gas emissions. The type of fuel used by a generator greatly affects its environmental impact. Generators running on diesel or gasoline tend to emit higher levels of greenhouse gases compared to those powered by natural gas.
If you’re concerned about reducing your carbon footprint, opt for generators that run on cleaner fuels like natural gas or consider exploring renewable energy options.
FAQ 3: Can I offset the greenhouse gas emissions from my generator?
Yes, you can offset the greenhouse gas emissions from your generator by purchasing carbon offsets. Carbon offsets are investments made in projects that reduce or remove an equivalent amount of CO2 from the atmosphere. These projects might include reforestation efforts or investments in renewable energy infrastructure.
By purchasing carbon offsets, you can neutralize the environmental impact of your generator’s emissions and contribute towards a more sustainable future.