Blackouts and permanent faults are just a few examples of power outages that wreak havoc to homes, hospitals, industries, and businesses. They can cut precious work time and inhabit devices that keep people safe.
The worst part is when power outages happen during electrically powered procedures. For example, imagine a patient under intensive care needing critical care and life support – and suddenly power goes off! A secondary power source can be lifesaving in such circumstances.
What is a Generator?
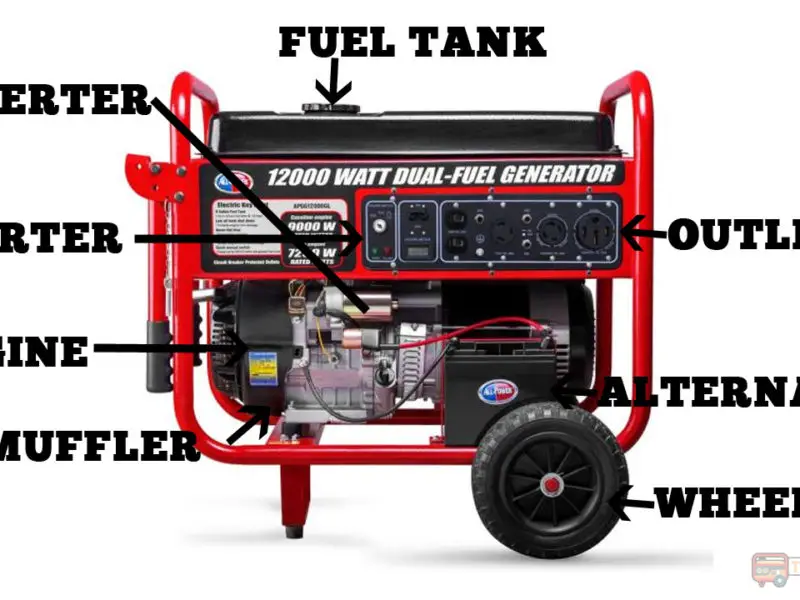
A generator is a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy for transmission and distribution over power lines to domestic, industrial, and commercial applications.
The mechanical power comes from various sources, such as hydraulic turbines at dams, waterfalls, wind turbines, steam turbines, gas turbines, and diesel engines.
Types of Generators
There are many ways to categorize generators. However, the three main types are as follows;
Portable generators are powered by gas or diesel fuel and can provide temporary electrical power. They are best used in refrigerators, nail guns, and spray gun systems.
Standby generators are electrical systems that operate with an automatic transfer switch that commands the unit to power a device when the power goes out. They are mainly used in hospital machinery and emergency settings.
- Inverter generator
Inverter generators use an engine connected to an alternator to produce alternating current power. They are mainly used to power laptops and car batteries.
Uses of Generators
Generators are now found everywhere, from residential to commercial and recreational applications. The following are the most common uses.
- Roadway vehicles
Motor vehicles require electrical energy to power their instrumentation, keep the engine operating, and recharge the batteries.
- Sailboats
Sailing boats may use water or wind-powered generators to charge batteries. A small propeller wind turbine connects to a low-power generator to supply current at typical wind speeds.
- Temporary power supply
It may be impossible to have dedicated power in some remote places or while organizing an event with no power grid. The only viable power source for such situations is an electric generator. These devices can power any electrical equipment, including tools, large lighting rigs, and sound systems.
- Backup power during outages
Power cuts and load shedding are commonly seen in rural areas during peak hours and severe conditions. A generator, being a source of independent electrical power, can keep the electrical systems alive in such times. It allows residents to continue their work without much interruption.
- Support to the main power source
Uses of generators can also include producing electricity within a specific period to support a power grid. For instance, the electricity demand may be high during peak hours, causing a supply shortage. When this happens, you can turn to generators to bridge the gap.
- Provide permanent power
Some facilities have to rely on generators for a permanent power supply. For example, in the agricultural sector, agricultural farms often require continuous electricity for performing different tasks from cultivating to harvesting and preserving crops. If such facilities don’t have easy access to the power grid, a generator would come in handy.
- Source of standby power
A standby generator provides electricity during emergencies. It remains idle during normal electricity supply but springs to action when the supply is interrupted. Standby generators keep everything running and prevent data loss in the event of unpredicted power failures. Even at home, a big worry during a power outage is food waste. Standby generators easily solve the problem.
- Prevent damages
A power outage when you are away from home can be costly. Having a generator allows you to keep the necessary appliances running in your home when there is a power failure. For instance, water damage is an ever-present concern during power outages. Backup generators can provide necessary heating to prevent potential damage.
- Recreational uses
Finally, we live in a digital world. Everyone is constantly on the phone, staying in touch with followers on social media, checking emails, watching videos, or reading a blog. Now, imagine when you have to go camping or boating! You’d still need a power source on your trip. Here too, a power generator can be precious.
Similarly, you can power an outdoor wedding using a portable generator, provide light for night games, power accessories such as electric blankets, and so much more.
Proper Maintenance is Key
Considering the above functions, it is important to know how to maintain your generator so that you can use it for a long time.
A few best practices include; checking the battery power, keeping an eye on the cooling system, annual fuel cleaning, and regular filtering. We also recommend regularly testing the battery’s current status and even the terminals and cables. Also, you must change the oil as per the manufacturer’s instructions. If you can ensure all the above, you can look forward to long battery life.